Managing people operations in today’s fast-paced workforce can be characterized by constant change, activity, and progress. How we optimize this change can lead to further growth in your organization. Therefore, it’s imperative to calculate your labor deviation score to have a predictive calculation as to how your people will perform.
However, calculating this score can be a cumbersome task. Managing employee schedules, union rules, vacation requests, call-offs, qualifications, training, and production lines is exhausting. With numerous moving parts to keep track of, how is someone set up for success when it comes to managing their people?
Automated dynamic scheduling technology is one strategic way to optimize scheduling, making it less of a headache. We refer to this as Dynamic Shift Scheduling and it’s the brains behind being able to calculate labor deviation scores.
Create an Optimized Schedule With Dynamic Shift Scheduling
Dynamic shift scheduling uses technology to consider all your scheduling inputs, leveraging an algorithm to create an optimized schedule for your workforce. Optimizing your schedule in a system that evaluates all of your needs means that when change happens (and it will), you can be proactive in adjusting your workforce assignments. There is no need to reference who is qualified or can fill a vacancy, everything you need to know is provided in a one-stop people operations shop.
Using a Dynamic Schedule optimized to follow your rules can give insight into better reporting. For example, our Labor Alignment Analytics tool allows you to see the past, present, and near future schedules compared to your demanded labor standards. This tool can help see overages, and shortages in your labor based on those labor standards. In addition, the Labor Alignment Analytics tool gives the ability to see where roster changes need to be made, how illness is affecting your labor pool, how last-minute demand creates an overresponse or shortage, and more.
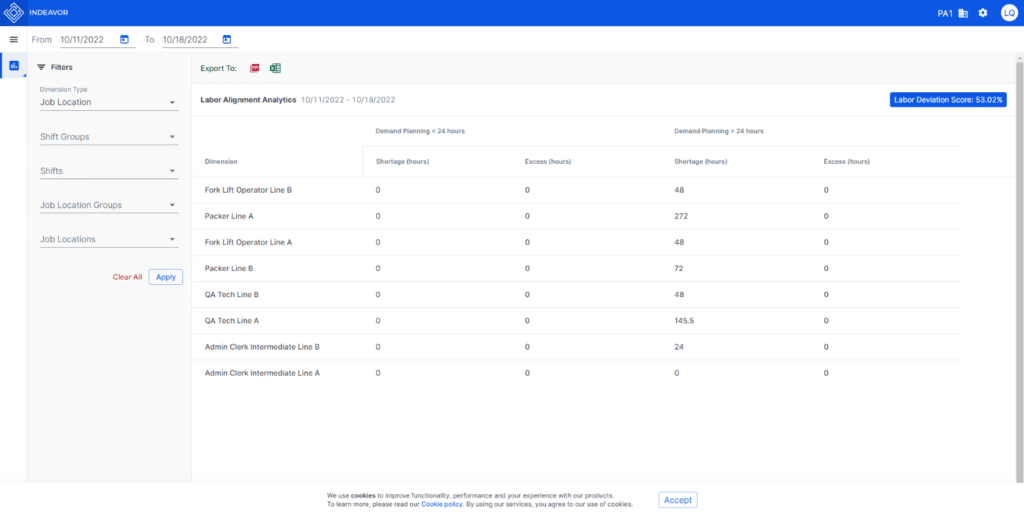
Automatically Calculate a Labor Deviation Score
Having insight into areas that need attention can benefit any enterprise.
Being able to measure that data across a single performance indicator is gold in terms of profitability. For example, we can develop a Labor Deviation Score by calculating all the overage and shortage hours against your total amount of demanded hours.
This Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is an easy indicator of the health of your people operations. Calculated as a percent, your Labor Deviation Score can show if you are 78% deviated from your labor standards, or 0% meaning your scheduled labor matches your labor standards. Demands have set labor requirements that your labor force must meet. If you are deviating from those demands, this KPI quickly sees it. Measured over time, this KPI can see if your changes improve your labor alignment.
Dynamic Scheduling is a way to optimize how you manage your labor force, giving you more insight into analytics and major KPIs. The Labor Deviation Score can be a heartbeat of your operations and show how well your labor is aligned with your demands.
Contact Indeavor today to discover and track your Labor Deviation Score.
About the Author
Luke Quadracci is a Senior Product Manager at Indeavor overseeing the advancement of our Reporting & Analytics products to better serve our customers. Connect with him on LinkedIn to learn more about Indeavor’s Solution.
Give us a call today to learn more about how Indeavor can help boost your productivity.







